The HIV Epidemic in Malaysia
The HIV epidemic in Malaysia is concentrated among 4 key populations (KPs), as below:
- People who inject drugs (PWID)
- Female Sex Worker (FSW)
- Transgender (TG)
- Men who have sex with men (MSM)
During the early phase, the country’s epidemic was driven by PWID bearing the impact of 70% – 80% of total reported cases annually but the trend has shifted to more sexual transmission since 2011. MSM is anticipated to become the main driver for the epidemic in the near future and more than 70% of HIV new infections are reported among people age 20-39 years old in 2017.
Malaysia is committed to End AIDS in 2030 as stated in the 2016 United Nations General Assembly Political Declaration on Ending AIDS. The UNAIDS strategic guidance on Fast Tracking to reach 90-90-90 by year 2020 was adopted to develop the National Strategic Plan for Ending AIDS (NSPEA) 2016-2030 that replace the National Strategic Plan (NSP) 2011-2015. NSPEA is also in line with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG). The NSPEA targeted four key strategies with the vision for Malaysia reaching zero new infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS related deaths.
The strategies are based on identified work in local context which is:
- Testing and treatment
- Improving the quality and coverage of prevention program among KP
- Reduction of stigma and discrimination
- Ensuring quality strategic information and its use by policy makers and planners through monitoring, evaluation and research
Surveillance of HIV/STI and behavioral risk factors should be the foundation of a country’s response to HIV. Unfortunately, the formal surveillance system and limited behavioral or ad hoc survey is still insufficient to adequately monitor the epidemic and risk trends in the country. Therefore ‘Integrated Bio-Behavioral Survey (IBBS)’ needs to be done periodically to reassess and adjust the surveillance system based on the information generated as well as assisting in impact assessment. IBBS is a community-based systematic survey designed to assess risk behaviors and the prevalence of HIV and other sexually transmitted diseases among the most-at-risk populations, in order to improve tracking of the HIV epidemic and program planning. By comparing data with the previous rounds, the IBBS surveys could assist in determining the epidemiologic pattern of the disease and risk behaviors trend in the country. The findings could also help the country to project and estimate the epidemic and disease progress over time which is crucial for better planning of preventive activities among KPs. The first IBBS was carried out in 2009 and it was the pilot phase of this survey.
Overview of the HIV & AIDS Epidemic in Malaysia

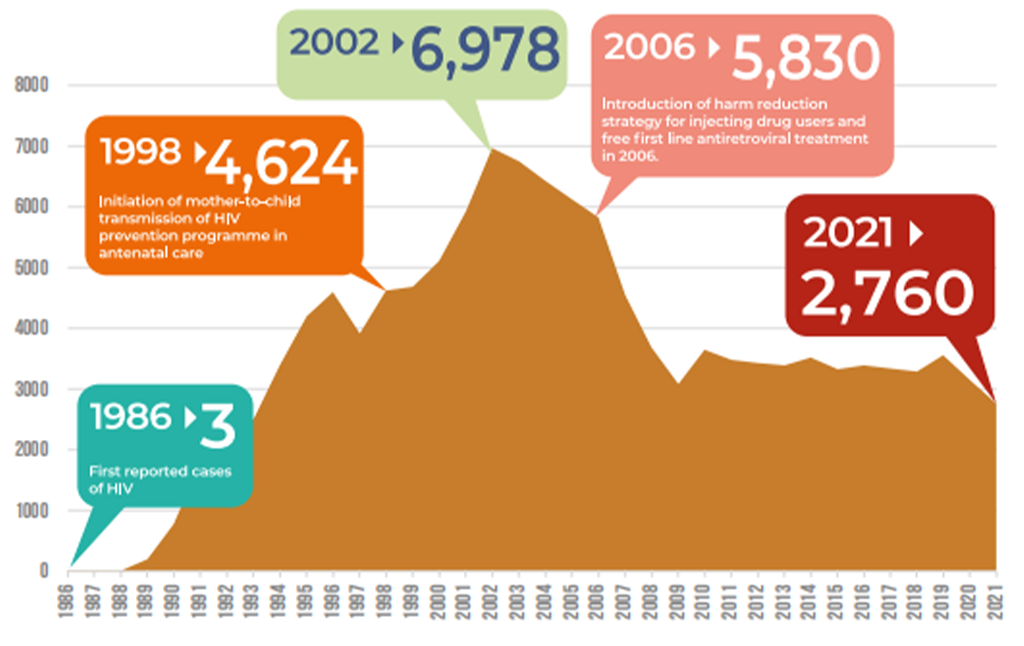
New HIV Cases (1986-2021)
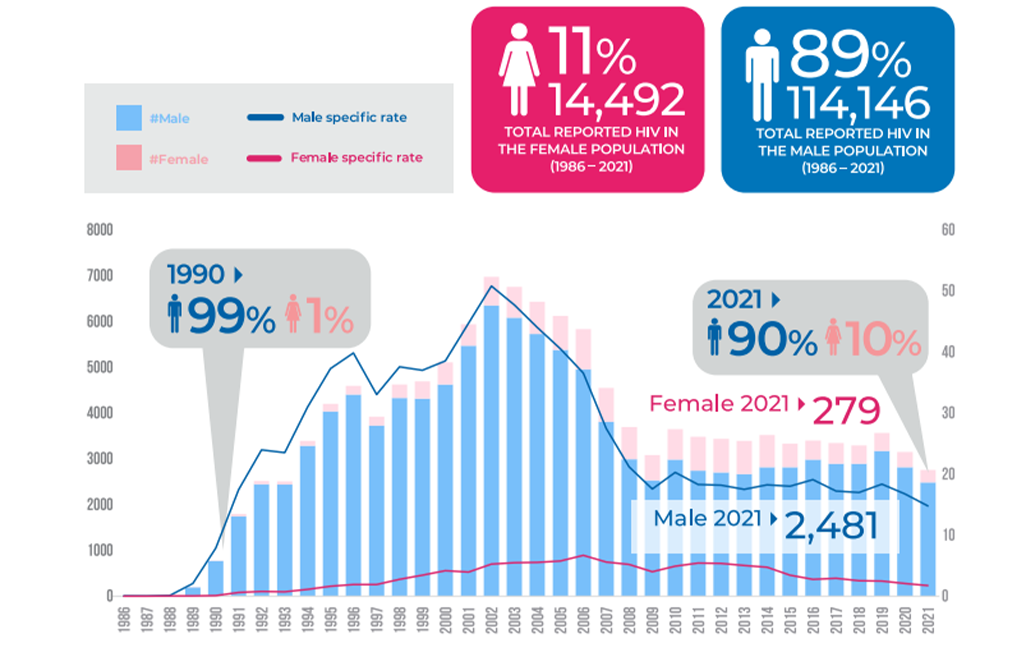
HIV Transmission by Gender (2021)
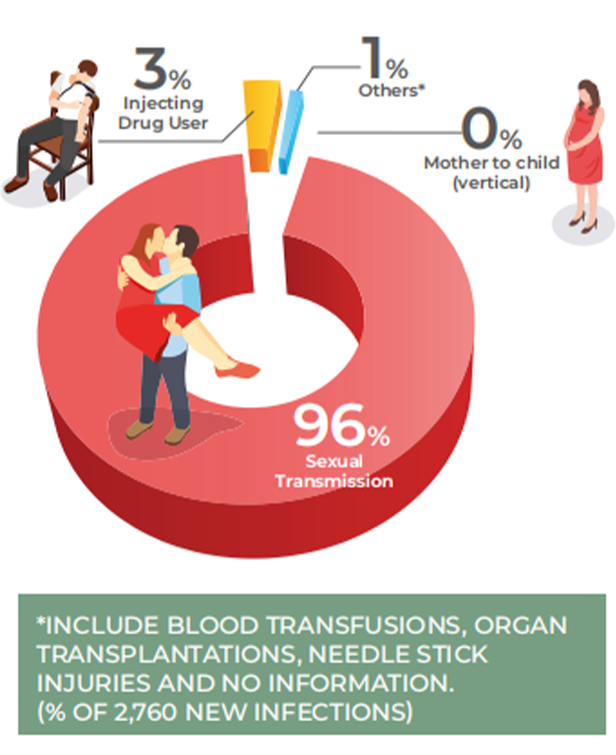
HIV Transmission by Risk Factor (2021)
HIV Transmission by Age (2021)

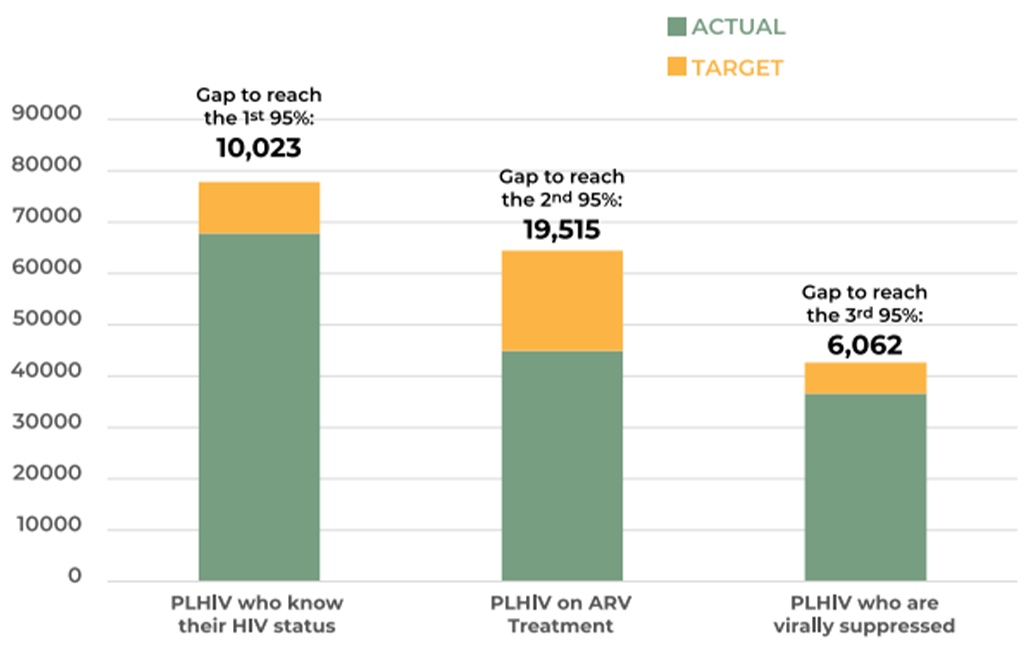
HIV Testing & Treatment Cascade (2021)
Comparison of New HIV Infections Between Injecting Drug Users (IDU) & Sexual Transmission (2005 - 2021)

Changes in HIV Landscape (1990 - 2021)

